Page Contents
Eating is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, providing nourishment and enjoyment. However, for many elderly individuals suffering from dysphagia, the act of swallowing can become challenging and even dangerous. Dysphagia is a medical condition characterised by difficulty swallowing, and it can affect people of all ages. In the elderly, it is often linked to age-related changes in the muscles and tissues involved in the swallowing process. Dysphagia poses significant risks, as it can lead to malnutrition, dehydration, and respiratory issues. One crucial aspect of managing dysphagia is paying attention to food textures and drink thicknesses. This is where EatSafe SG comes into play.
Complications of dysphagia
Dysphagia extends beyond the challenge of swallowing itself, bringing with it a host of potential complications that demand careful consideration. One significant concern is malnutrition, a consequence of inadequate nutrient intake resulting from difficulties in eating. As individuals with dysphagia may struggle to consume a balanced diet due to limitations in food textures and drink consistencies, they become more vulnerable to nutritional deficiencies, compromising their overall health.
Another critical complication associated with dysphagia is aspiration pneumonia. This occurs when food, liquid, or saliva enters the airway instead of the esophagus, leading to infection in the lungs. Aspiration pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, underscoring the importance of managing dysphagia effectively to prevent respiratory complications.
Choking is yet another risk that individuals with dysphagia face during meals. The difficulty in swallowing increases the likelihood of food or liquid entering the windpipe, obstructing the airway and causing choking. This not only poses an immediate danger but also heightens anxiety around meals, potentially leading to a decreased appetite and further exacerbating the risk of malnutrition.
The role of EatSafe SG
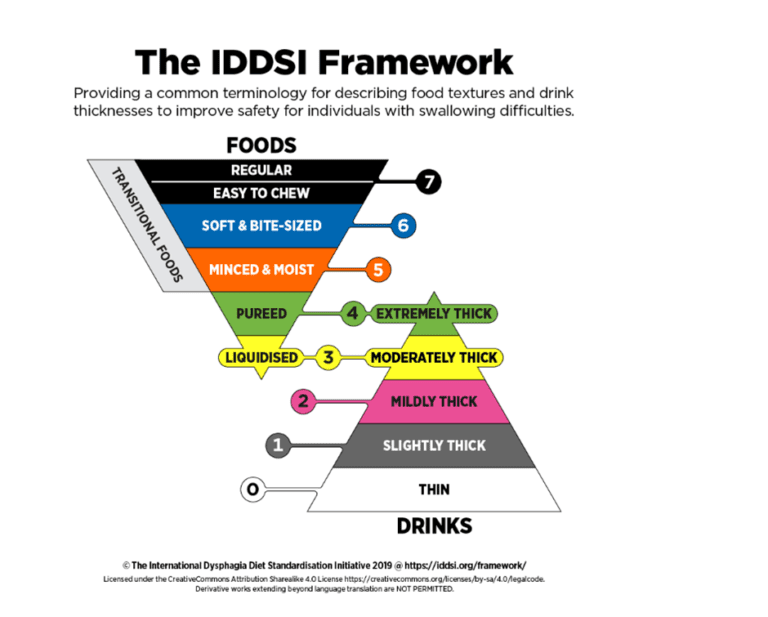
EatSafe SG is a comprehensive program referenced from the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) framework (www.iddsi.org) to address the specific needs of individuals with dysphagia (Figure 1). It provides a range of resources and guidance to ensure that elderly individuals with dysphagia can enjoy their meals safely.
Texture and thickening guides
EatSafe SG offers detailed guides on appropriate food textures and drink thickness levels. These resources empower caregivers, healthcare professionals, and individuals with dysphagia to make informed choices about meal planning.Food preparation resources
The program provides a reference guide for food preparation staff or chefs on how the standard raw ingredients and local food can be modified to meet IDDSI levels.Training and support
EatSafe SG provides training modules and support for caregivers and healthcare professionals, helping them understand the challenges of dysphagia and implement strategies for safe and enjoyable eating.
The objectives of EatSafe SG are to:
- Improve patient safety.
- Improve communication within and between healthcare professionals, healthcare providers and patients by reducing misunderstandings and ambiguity when communicating diet or fluid related information.
- Adopt standardised diet and fluid labels and descriptors when conducting and publishing research that is aligned to an international framework.
Managing food textures
Soft and moist foods
Soft and moist foods are easier to swallow for individuals with dysphagia. These include mashed potatoes, yogurt, and well-cooked vegetables. These textures reduce the risk of choking and aspiration, ensuring a safer eating experience.
- Pureed foods
For those with more severe dysphagia, pureed foods are often recommended. These foods have a smooth, pudding-like consistency, making them easier to swallow and reducing the effort required during the swallowing process.

- Avoidance of tough or dry foods
Foods that are tough or dry can be challenging for individuals with dysphagia to manage. It’s crucial to avoid foods like tough meats, dry bread, and crunchy snacks, as these can increase the risk of choking.
Managing drink thickness
Thin liquids
Thin liquids, such as water and clear broths, can be challenging for individuals with dysphagia to control during swallowing. These liquids may easily enter the airway, leading to aspiration. It is advisable to thicken liquids to a more manageable consistency.Thickened liquids
Thickening liquids using products like thickening agents or commercial thickeners can make them safer for individuals with dysphagia. This modification helps control the flow of the liquid, reducing the risk of aspiration and ensuring a safer drinking experience.
Conclusion
Ensuring the safety and enjoyment of meals for elderly individuals with dysphagia requires attention to detail, especially regarding food textures and drink thicknesses. EatSafe SG plays a pivotal role in this process by providing resources and guidance that emphasise safe and appropriate food textures and drink consistencies, thereby reducing the risks of malnutrition, aspiration pneumonia, and choking. By addressing these complications head-on, caregivers and healthcare professionals can enhance the overall well-being of individuals navigating the challenges of dysphagia, fostering a safer and more satisfying dining experience, and improving their quality of life.
