Page Contents
Insulin is a hormone produced by pancreas that serves 3 important functions:
- Regulates the glucose level in your blood stream.
- Converts excess glucose to glycogen and store in your liver, lipid (fat), and skeletal muscles.
- Regulates the carbohydrates, lipid, and protein metabolism.
In this article, we look at the importance of insulin therapy for people with diabetes.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes
There are two common types of diabetes, namely type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition where immune system attacks the islets in pancreas, stopping the production of insulin. This diabetes is caused by genetic mutations during childhood or adolescence. Studies show that genetic factors can pre-dispose people to developing type 1 diabetes, but almost 90 percent of people who develop type 1 diabetes do not inherit the condition from parents.
Type 2 diabetes is another chronic condition appears mostly with people with sedentary lifestyle, overweight, and obese. In this type of diabetes, insufficient insulin is produced in the body, and there is resistance in target tissues such as muscle, liver, and fat, also known as insulin resistance.
What happens if there is no insulin?
If there is no or insufficient insulin, or insulin is not functioning optimally in your body, you will soon develop diabetes. Diabetes is a condition where the sugar level in your bloodstream is relatively higher than ordinary people. If diabetes is left untreated, over time, it can lead to multiple health implications. For example, damage of blood vessels and nerves leading to impaired wound healing and organs failure.
People with type 1 diabetes requires an external supply of insulin, while only some people with type 2 diabetes need to take insulin. Often, people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood sugar level with the help of proper diet and lifestyle modifications, and oral medications.
Types of insulin
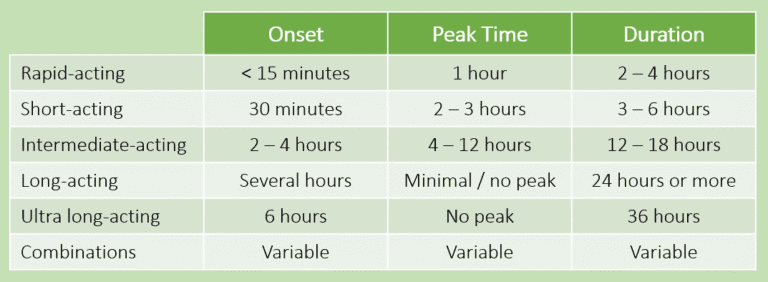
Insulin is usually categorised by 3 characteristics:
- Onset: how quickly insulin kicks start the effect.
- Peak time: when insulin is most effective.
- Duration: total time for insulin to wear off.
There is no single type of insulin that can meet different needs of different people. The 5 common types (and combinations) are shown in Figure 1. Click here for more information on insulin.
Options of insulin therapy
- Conventional insulin injection
Injection of insulin is delivered using syringe. Sometimes requires the mixing of insulin from 2 vials / bottles. - Insulin pen
A pre-loaded, portable, and convenient pen for the delivery of insulin compared to having to draw from vial using a syringe. - Insulin pump
A portable computerised device that delivers insulin through a thin tube that goes under your skin. The device delivers insulin through a steady flow throughout the day and night (basal insulin), and an extra dose at mealtime (bolus). - Insulin patch
Deliver rapid-acting insulin under your skin through an insulin-containing patch. It contains a fixed dose of insulin that is absorbed over a number of hours. This insulin patch eliminates the need for multiple daily injections.
Depending on your overall assessment on type 2 diabetes, your doctor will decide whether to use insulin or glycemic control medication. There are 6 types of non-insulin oral medications for the treatment of type 2 diabetes:

Conclusion
In prediabetes stage, your doctor will prescribe diet and lifestyle modifications to manage your condition.
In type 2 diabetes cases, doctors usually first recommend non-insulin oral medications, e.g. Metformin. If diet and lifestyle modifications together with oral medication are not effective in managing your blood sugar, doctor will prescribe insulin therapy.
As treatment technology evolves, the conventional way of preparing and mixing insulin from vial(s) and injecting through a syringe has been gradually replaced by easier methods, such as insulin pen, insulin pump, or insulin patch.
For diabetic patients who are obese, doctors may suggest weight loss surgery such as metabolic surgery or bariatric surgery (gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy).
