Page Contents
Abraham Maslow was an American psychologist who developed the Hierarchy of Needs theory in the 1940s. This theory outlines five different levels of human needs that drive behaviour, these needs must be fulfilled in order to achieve self-actualisation, or the realisation of one’s full potential. While this theory was initially developed for young adults, it is still relevant today and can be applied to all stages of life, including the elderly population. In this blog article, we will explore Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and its relevance to the elderly.

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
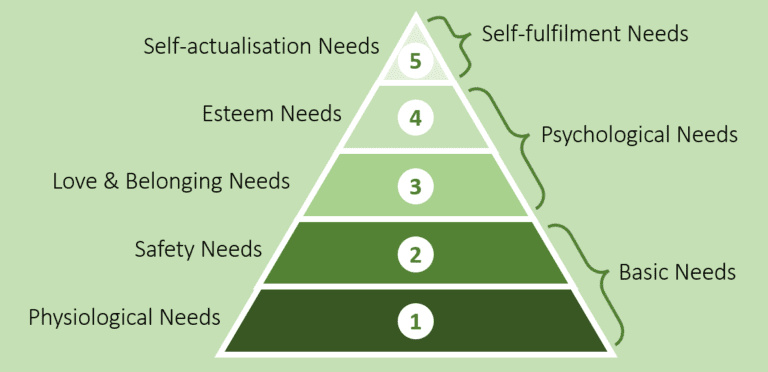
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs consists of five different levels, with the most basic needs at the bottom of the pyramid and the most complex needs at the top (Figure 1). The levels are as follows:
- Physiological needs
These are the most basic needs that must be met in order to survive, such as food, water, shelter, and sleep. - Safety needs
Once physiological needs are met, people require a sense of safety and security. This includes physical safety, financial security, and emotional stability. - Love and belonging needs
Humans are social creatures and require love and a sense of belonging. This includes friendships, romantic relationships, and a sense of community. - Esteem needs
Once the previous needs are met, individuals require a sense of self-esteem and respect from others. This includes recognition, achievement, and status. - Self-actualisation needs
This is the highest level of need and refers to the realisation of one’s full potential. It includes creativity, problem-solving, and the pursuit of personal growth.
Applying Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to the elderly population
As we all age, our needs will gradually change, and the focus shifts from meeting the basic physiological needs to fulfilling higher-level needs such as self-actualization. The same actually applies to elderly population. In order to apply Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to them, it is necessary to understand how the elderly’s needs change over time.
Physiological Needs
The physiological needs of the elderly are similar to those of younger people. They need food, water, shelter, and sleep to survive. However, elderly people may require more attention to their physical needs due to their declining health. For example, elderly individuals may require specialized diets or medications, and they may need assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs) such as bathing, dressing, and using the restroom.
Safety Needs
As older people have declining physical abilities, they are more vulnerable to accidents and injuries. Elderly people need to feel safe and secure in their own environment. Therefore, safety needs become increasingly important for the elderly population. This includes ensuring that their living environment is safe and accessible, they may require assistive devices, such as grab bars or wheelchair ramps, to prevent falls and injuries. They also require adequate medical care, and ensuring that they are protected from financial scams, abuse, and negligence. Meeting these safety needs can provide a sense of security and peace of mind, which can enhance their overall well-being and quality of life.
Love and Belonging Needs
Elderly individuals may experience social isolation and loneliness especially when their partner pass away, this can have negative impacts on their mental and physical health. Social support can come from family members, friends, or caregivers. This includes maintaining relationships with family and friends, participating in social activities, and being part of a supportive community. Social support and interaction can improve their mood and provide a sense of purpose and belonging.

Esteem Needs
As people age, their sense of identity may shift, and they may no longer derive their self-esteem from the common sources such as career success or physical appearance. Nonetheless, they still need to feel valued and respected by others. Esteem needs can be met through positive feedback and recognition of their accomplishments. Therefore, it is important to recognize and celebrate the achievements and contributions of the elderly population, and to provide opportunities for them to engage in meaningful activities such as volunteering or mentoring younger people, these would help them maintain their sense of self-worth.
Self-Actualisation Needs
While self-actualisation needs may seem less relevant to the elderly population, they are still important for maintaining a sense of purpose and fulfillment. Some elderly people may still have unfulfilled aspirations or desires. They may have unfinished projects or goals that they want to accomplish. Self-actualization needs can be met through opportunities for personal growth and development, such as pursuing hobbies, learning new skills, volunteering, contributing back to society, or engaging in creative pursuits such as writing or painting. Being able to fulfill their self-actualisation needs can provide a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction.

Conclusion
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a useful framework for understanding the evolving needs of the elderly population. Meeting their physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualisation needs can improve their overall well-being and quality of life.
Elderly people have unique needs and challenges, but they can still benefit from the same basic human needs that motivate all people. Caregivers, family members, and healthcare providers can use Maslow’s theory to guide their interactions with elderly people and promote their overall health and happiness.
