Page Contents
Tea is the second most consumed beverage that people of different cultures, different countries, drink for thousands of years.
If you are a tea lover, you would have known the health benefits of drinking tea. However, are you aware that some people may have been drinking tea the incorrect ways?

Different types of tea
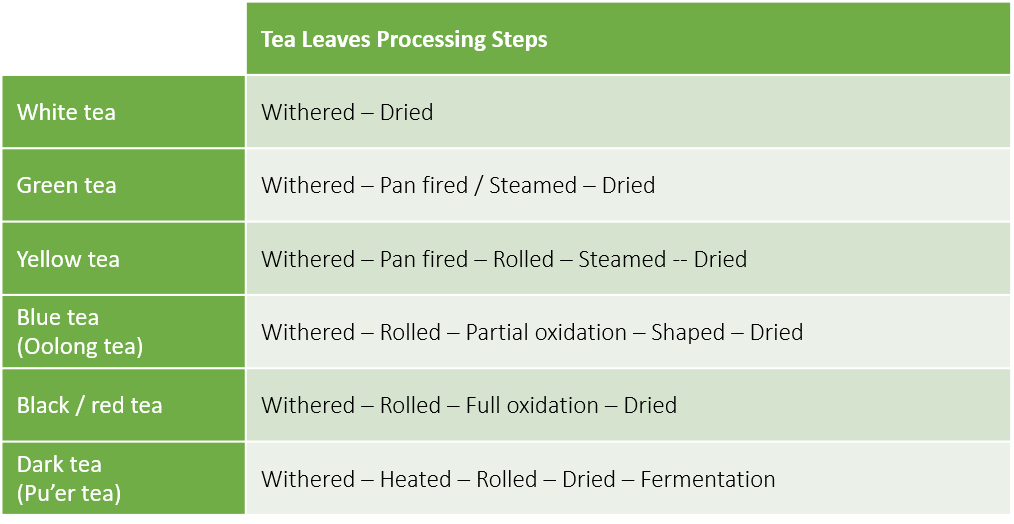
The “true tea” comes from Camellia sinensis plant. Tea masters use delicate methods to process tea leaves, including:
- Withering
- Inducing enzymatic oxidation (rolling, shaping or crushing)
- Stopping oxidation (steaming, pan-firing or roasting)
- Microbial fermentation.
Combinations of various processes and the amount of oxidation determines the different types of tea is produced (Figure 1). More information can be found here.
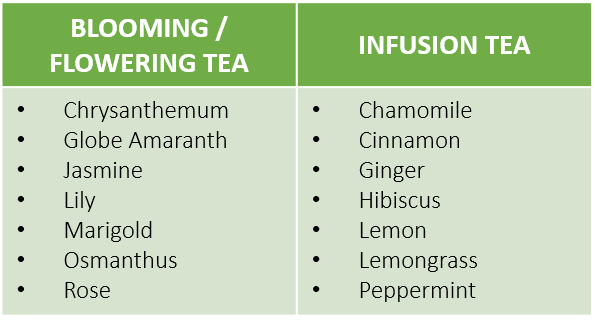
There are also teas that are not made solely from tea leaves. For examples, infusion tea and blooming / flowering tea (Figure 2). The main difference is that in blooming tea, the floral bulbs expand and unfurl beautifully when steeped (Figure 3). While infusion tea places more attention on the aromas and colours that produced from a flavourful ingredients.

Other popular teas are such as Chai tea that is made of black tea with aromatic herbs and spices. Kombucha that is produced by fermentation of sweetened black tea using a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast.
What are the health benefits?
Tea is rich in flavonoids (catechins, thearubigins, theaflavins, and quercetin) that have been proven to have beneficial effects against diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, hypertension, etc.
- Cardiovascular disease
Flavonoids are associated with strong protection against atherosclerosis, which is the underlying factor for heart attacks and ischemic strokes. High concentration of amino acid theanine in tea is also helping to protect against stroke. - Hypertension
Green tea has shown promising anti-hypertensive benefits through relaxing the smooth muscle that lines blood vessels. - Obesity & type 2 diabetes
Green tea extracts, EGCG and catechins, are reported to help with weight loss by increasing basal metabolic rate, improving glucose uptake by muscle, and enhancing fat-burning in the liver and muscle. Catechins can also reduce haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) which high HbA1c is an indicator of diabetes. - Cancer
Although there has not been substantial and conclusive evidence yet, early clinical studies suggest that the strong antioxidant properties of polyphenols in tea may help in cancer prevention, in particular, cancer in biliary tract, breast, endometrial, liver, and oral. - Anti-ageing
The antioxidants in tea can reduce inflammation, reduce the breakdown of collagen and elastin, which then lessen the formation of wrinkles, and slow down the natural ageing process.
Other popular and well-accepted health benefits of tea are such as improving digestion, slimming, refreshing and calming, boosting immunity, and so forth.
Does it have any side-effects?
Undeniably, drinking tea has shown many beneficial health effects. But is tea really the magic bullet for major illnesses? Well, not really, if you drink it the wrong way. Here is a list of unhealthy ways of drinking tea.
- Brewing tea for too long
Keeping tea leaves in boiling hot water for too long will destroy the vitamins and bioactive compounds. - Drinking strong tea
Steeping too much tea leaves into a cup will make the tea darker and more bitter. At the same time, it can release high amounts of caffeine and tannins. High-dose ingestion of tannins may cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, and liver damage. - Drinking too much tea
Moderate drinking is healthy for most people, but drinking too much tea could also lead to negative side effects, such as anxiety, headaches, digestive issues, and disrupted sleep patterns. - Drinking tea when empty stomach
Drinking tea on an empty stomach can cause nausea and an upset stomach. This is because tannins in the tea stimulates the secretion of gastric acid, the situation can be serious if you suffer from peptic ulcer or acid reflux problems. - Drinking tea after a meal
If you drink tea immediately after a meal, tannins can restrict your body’s absorption of iron from the foods (e.g. red meat, seafood, spinach, legumes, etc.). - Drinking tea before bed
Even though caffeine content in tea is not as high as coffee, drinking too much tea (especially black tea) before bed can spike up your caffeine level and keep you awake and disrupt your sleep pattern. - Drinking sweetened tea
Tea is naturally bitter. Many people drink it with sugar or artificial sweetener. Over-consumption of sugar or sweetener may have health damaging effects such as headache, depression, increased cancer risk, weight gain, impact on gut health, and increased risk of diabetes. - Drinking bottled or canned tea
Ready-to-consume bottled or canned tea is very convenient. However, there is also preservative added to keep the content fresh. Long-term consumption of preserved drinks is known to have negative health impacts.
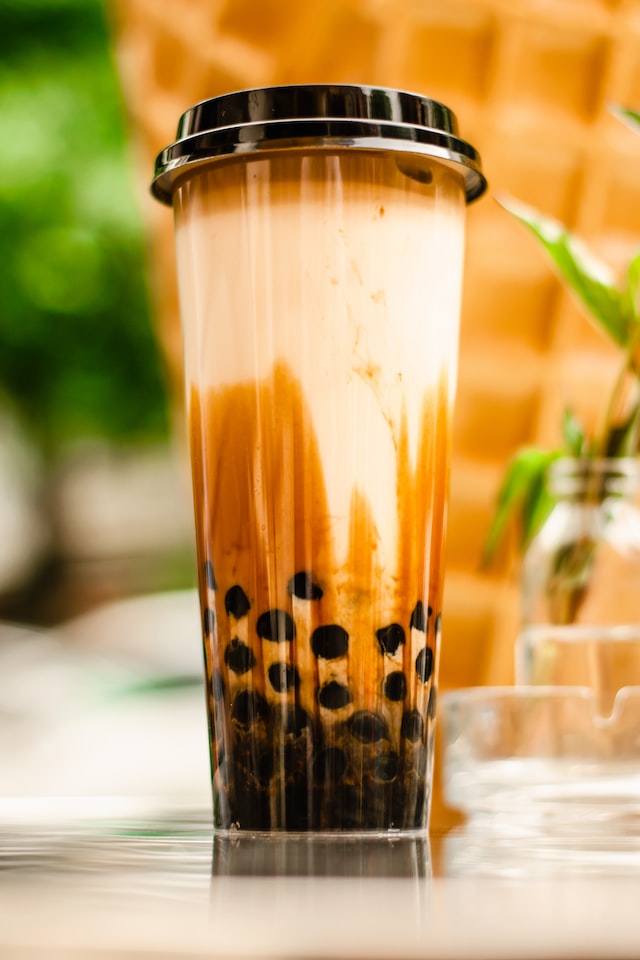
What about bubble tea?
It is very common nowadays to see younger generations so obsessed with bubble tea (boba tea). New stalls open one after another, and you will always see youngsters queuing and buying every day.
Bubble tea originated from Taiwan, it is a tea-based drink blended with milk, fruit, fruit juices, and a lot of chewy black tapioca pearls that fill almost half the cup.
Unlike other teas, bubble tea provides nearly no health benefit. In most cases, bubble tea is very high in sugar content, which long-term consumption can lead to chronic health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, heart diseases, stroke, kidney failure, and so on.

Conclusion
After knowing the different types of teas and their health benefits, you may keen to start appreciating tea. But, do also take note of the wrong ways of drinking, which may bring you more harm than benefit.
Last but not least, if you are a bubble tea lover, think twice before you order your next cup. You may enjoy the instant gratitude of drinking bubble tea, but in long run and when you age, the chronic impact on your health will start to surface one after another.
