Page Contents
Prevalence of diabetes is a major health concern nowadays due to unhealthy diet and lifestyle. We shared about the chronic conditions related to sugar, and also diabetes in previous blogs. As self-monitoring of blood glucose is an essential step in diabetes management, we discuss how to measure blood glucose using a glucometer at home in this article.
Importance of monitoring blood glucose
For the safety of someone with diabetes, it is crucial to monitor and maintain blood glucose at a safe level. Measuring blood glucose can:
- Let you know the level of blood glucose at a given time. In turn, determine whether you are normal, hypoglycaemic or hyperglycaemic.
- Find out if your diet, lifestyle, exercise, stress, and medications affect your blood glucose.
- Knowing your blood glucose level can help you adjust the amount of insulin injection needed.
- Help your diabetes management team to strategise the best management regime for your diabetes.
Hyperglycaemia
Hyperglycaemia is also known as high blood glucose. This usually happens when your body has insufficient insulin or when the insulin is not working properly, causing the blood glucose level shooting up to 10 mmol/L and beyond. Early symptoms include frequent urination, feeling thirsty, blurred vision, and fatigue. If left untreated, it can turn to ketoacidosis with fruity-smell breath, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, confusion, and potentially loss of consciousness.
Hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia is a condition that your blood glucose is 3.9 mmol/L and below. When your blood glucose gets too low, you will experience shakiness, lightheadedness, nausea, turning pale, sweating, irregular or fast heartbeat, etc. Severe hypoglyceamia can even lead to confusion, blurred vision, seizures, and loss consciousness.
Measuring blood glucose
Glucometer
Glucometer is a portable and home-based device that measure your plasma or whole blood glucose level from a tiny drop of blood obtained from finger prick. Finger prick is done by piercing a lancet under your skin at your fingertip so that blood can be extracted for quick glucose testing.

HbA1c test
Unlike the the home glucometer, HbA1c test which is usually performed in hospital or laboratory, measure the average of your plasma glucose level over 3 months period. The result is about 10 to 15 percent higher than home glucometer test.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
As compared to HbA1c test, OGTT is more sensitive. This test aims to measures your body’s response to sugar. It provides more information of the pathology of uncontrolled post-meal blood glucose. Similar to HbA1c test, OGTT can only be tested in hospital or diabetes clinic.
When to measure blood glucose at home?
Regular blood glucose monitoring is important to manage type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In the initial period, your healthcare team will advise you to record your blood glucose at different occasions. For example, after you wake up in the morning, before and after meals, after eating different foods, after taking your prescribed medicines, after exercise, at bedtime, etc.
Once your healthcare team analyse your blood glucose levels at different events, they will be able to advise you a suitable schedule and frequency of monitoring, as well as the right amount of medications or insulin for injection. Most people with type 2 diabetes only need to check their blood glucose once or twice a day. If your blood glucose level is stable and under control, you may reduce to check a few times a week.
How to use a glucometer?
Performing a self-test using glucometer is quite easy. You will remember the steps after a few practices. Here are the steps:
- Preparing glucometer
- Make sure the glucometer is clean and ready to use.
- Code the meter whenever a new box of test strips is opened.
- After taking out a test strip, immediately close the container tightly to prevent moisture.
- Set your glucometer with your preferred unit of measurement (mmol/L or mg/dL).
- Preparing for finger prick
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water and disinfect finger with alcohol swab.
- Dry and massage your hand to get blood into your finger.
- Use a lancet to prick the fingertip and squeeze from the base of the finger.
- Hold a drop of blood to the edge of the test strip until blood is transferred to the strip.
- Reading blood glucose
- Slot in the strip in the glucometer.
- The blood glucose result will be displayed in the measurement unit as set (mmol/L or mg/dL).
- Record the reading
- Record your results and add remarks if there is anything you have done differently (e.g. after certain foods, after exercise, medications, etc.).
- Clean up and storage
- Remove test strip from the glucometer.
- Properly dispose the lancet and strip in a puncture-proof container.
- Avoid exposing test strip to moisture, extreme heat, or cold temperatures.
Some facilities test the first drop of blood as it is. Others may wipe away the first drop with gauze and test the second drop. This is because some believes the first drop of blood might come in contact with the alcohol swab and alcohol may affect the values.
How to read a glucometer?
Depending on the model or brand of the glucometer, usually a glucometer provide readings of blood glucose level in mmol/L or mg/dL.
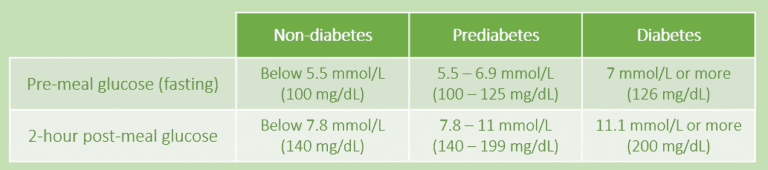
As shown in Figure 1, a healthy (non-diabetic) person would have the fasting blood glucose below 5.5 mmol/L, while below 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after meal.
If your blood glucose is within the 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/L range before meal or 7.8 to 11 mmol/L after meal, you are likely to be prediabetic. It is safer for you to consult your doctor on possible dietary, lifestyle, or medication modification.
However, if your fasting blood glucose often falls beyond 7 mmol/L or more, and above 11.1 mmol/L 2 hours after meal, you could be diabetic, you should consult your doctor as early as possible.
After knowing your blood glucose level
To facilitate your healthcare team in crafting a better diabetes management plan, you can keep a record of your blood glucose levels at various occasions as mentioned earlier. This can be done through manual paper record, using excel spreadsheet, mobile phone applications, or the software associated with your glucometer.
If you are diabetic, you may not be carrying a glucometer everywhere, but you should always bring with you 2 things:
- Diabetes medications or insulin pen in case of hyperglycaemia.
- A few sweets, fruits, or sugary drinks in case of hypoglycaemia.
Conclusion
Apart from regular self-test using glucometer, you should also get a HbA1c test or OGTT test at least once a year to have a better picture of diabetes condition.
If you are healthy or prediabetic, maintaining your blood glucose level within the optimal range is important to minimise your risk of developing diabetes-related complications. You can achieve a better blood glucose target by:
- Maintaining healthy diet.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle.
- Adhering to diabetes management regime.
