Page Contents
Coffee is the third most consumed beverage in the world after water and tea. It has a rich aroma and consists of over 1000 bioactive compounds:
- Alkaloids (caffiene, trigonelline).
- Phenolic compounds (chlorogenic acid (CGA), diterpenes, cafestol, kahweol, anthocyanins, lignans, , etc.).
- Lipids (triacylglicerols, terpene esters, sitosterol).
- Carbohydrates (sucrose, galactose, glucose, fructose).
- Minerals (magnesium, potassium, copper, calcium, aluminium, phosphorus).

4 things that make your coffee different
Have you ever wonder why is there such a wide variety of coffee types? How do they differ from each other? There are basically 4 things that make up the type of coffee you drink.
(1) Coffee Beans
There are 4 main types of coffee beans:
- Arabica bean (from East Africa), about 60% of the coffee in the market.
- Robusta bean (from Africa, Indonesia, India), about 40% of the coffee in the market.
- Liberica bean (from West Africa), rather rare, about 2% of the coffee in the market.
- Excelsa bean (from Southeast Asia, India), reclassified as subtype of Liberica bean.
(2) Degree of Roasting
How much the coffee beans are being roasted will determine the colour, taste, aroma, and acidity.
- Light Roast (pale brown) coffee beans are more aromatic and have good acidity.
- Medium Roast (medium brown) beans give more sweetness, nuttiness, and less acidity.
- Medium-dark Roast (dark brown) has stronger flavours of chocolate and nuts, but with no acidity.
- Dark Roast (black) coffee beans have bitter, nutty, chocolatey and toasty flavours, with no acidity.
(3) Grinding and Brewing Methods
Before brewing, a grinding process is used to break the roasted coffee beans into coarse or fine ground. Coarse coffee grounds are more suitable for cold brew, French press, percolators, Chemex, drip coffee brewing methods. While fine grounds have bigger surface area and more intense flavour. It is more suitable for pour-over, espresso maker, and Turkish coffee brewing methods.
When water passes through, it can extract the oils and flavours fully. The extraction method here refers to brewing. There are different methods of brewing as shown in the table below (Figure 1).
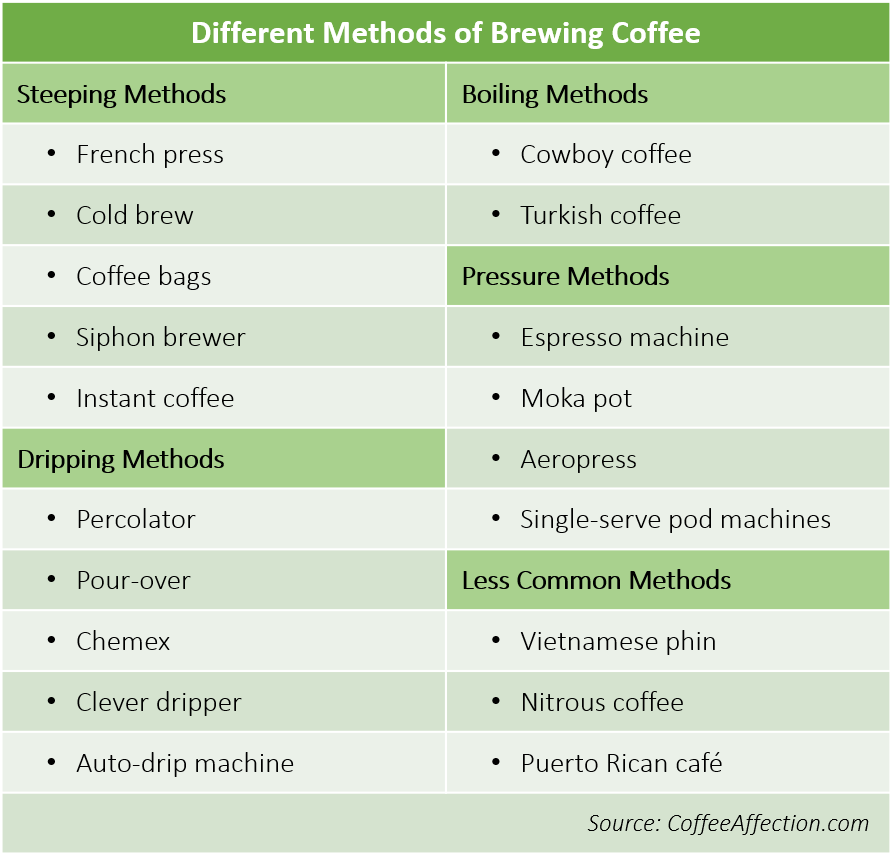

You can click here for more information on the different brewing methods.
(4) Taste and texture enhancements
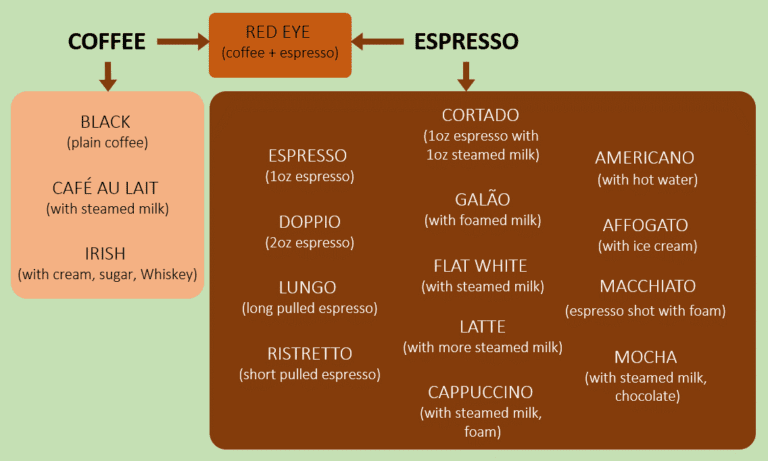
After brewing, you will get the liquid extract of coffee. Depending of the ground to water ratio, you will either have coffee (less intense) or espresso (more intense). With the additional of water, steamed milk, milk foam, sugar, cream, chocolate, etc., you can enrich the flavour and experience of your cup of coffee (Figure 2).

Health benefits of drinking coffee
Coffee contains approximately 1000 bioactive compounds with some of them are strong antioxidants. Drinking coffee is known to have many health benefits, such as:
- Lower the risk of type 2 diabetes by reducing the hemoglobin A1C.
- Reduce the risk of heart disease by protecting against arterial damage caused by inflammation.
- Lower risk of cancer, e.g., prostate, endometrial, liver, colon, breast, and rectal cancers.
- Protect against Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other types of dementia.
- Temporary boost the brain activity, concentration, and memory.
- Lower the risk of cirrhosis (liver scarring).
- Enhance exercise performance by strengthening muscle contraction, and increasing fatty acids in the blood, which leads to better endurance.
- Prevent depression by activating dopamine and serotonin (happy hormones).
Does it have any side-effects?
On the other hand, there are also opposing evidences that report the disadvantages of consuming too much coffee (coffee overdose). Most of these are related to caffeine. For example:- Acutely decrease insulin sensitivity.
- Cause irritability, nervousness or anxiety.
- Transiently increase heart rate, raise blood pressure, causing palpitations and tremors.
- Affect sleep quality and cause insomnia.
- Rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown) leading to kidney failure.
- Over stimulate bowel movements, causing loose stools or diarrhoea.
- Increase urination, lead to thirst and dehydration.
- Frequent urination also causes loss of minerals such as sodium, chloride, calcium. Leading to bone loss in elderly.
- Erode the enamel of teeth, causing sensitivity and cavities.
- For pregnant women, it may cause preterm labour and low birth weight of infant.
Is decaffeinated coffee really better?
In view of the reported side-effects of caffeine, there is an alternative known as decaffeinated coffee (97% of caffeine is removed). Decaffeinated coffee is made by steaming and repeatedly flushing away the caffeine using chemical solvent such as ethyl acetate or methylene chloride.
Drinking decaffeinated coffee might avoid the signs and symptoms of overdosing. However, decaffeinated coffee is not entirely the healthier choice. There are some negative effects of regular drinking of the decaffeinated coffee.
- At high dose, it can cause headache, confusion, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and fatigue.
- It increases the levels of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol).
- Chemical solvent (methylene chloride) could be carcinogenic to human.
- It may aggravate rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- It also increases the concentration of serum gastrin that triggers the release of stomach acid.
- Disrupt iron absorption.
What types of coffee you should avoid?
Nowadays, there are so many other unhealthy coffee in the market. Long-term consumption will lead to many negative health impacts. Here are some examples:
- Instant and soluble coffee contain higher amount of cancer-causing acrylamide than freshly roasted coffee.
- Drinking sweetened coffee, either by adding too much sugar or sweetened condensed milk may cause diabetes.
- Frappuccino taste great, but it is outrageously high in saturated fat, processed sugar, and calories. Over consumption will lead to heart problems, diabetes, obesity, and so forth.
Conclusion
Everyone responds to caffeine differently, some show no effect, and some have over-reaction. If you are experiencing any negative effects or prolonged discomfort, you could have been over-dosed. You may try reducing your coffee consumption or drink a less intense coffee.
It is important to taper your consumption gradually instead of quitting it cold turkey after you have built physical and psychological dependence. Sudden quitting can lead to caffeine withdrawal symptoms that may include severe headache, restlessness, muscle aches, and fatigue as commonly seen in many addictions.
