Page Contents
In recent years, the approach to eldercare has undergone a significant transformation. The focus is shifting from curative medicine, which aims to treat diseases and ailments after they occur, to preventive healthcare, which seeks to prevent these conditions before they develop. This change is especially relevant to the young-old population (those between 65 and 74 years old), who stand to benefit the most from preventive strategies. This blog explores the definitions of these two approaches, the transitions within the eldercare sector, and a comparison of their advantages and disadvantages to determine which model is better suited for today’s eldercare needs.
Curative medicine vs preventive healthcare
Curative medicine, also known as reactive or therapeutic medicine, focuses on diagnosing and treating illnesses and diseases. This traditional approach involves medical interventions, such as surgeries, medications, and other treatments, aimed at curing or managing health conditions. The primary goal is to restore health after a problem has been identified. While curative medicine has achieved remarkable success in treating acute conditions and life-threatening diseases, it often addresses health issues only after they have become serious.
Preventive healthcare emphasises measures taken to prevent the onset of diseases and health issues before they occur. This approach includes lifestyle modifications, regular screenings, vaccinations, and early detection strategies. Preventive healthcare aims to maintain health and well-being by reducing risk factors and promoting healthy behaviours. The emphasis is on education, awareness, and proactive management of health to avoid the development of chronic conditions and improve overall quality of life.

Transitions in the eldercare sector
The eldercare sector is gradually transitioning from a reliance on curative medicine to a more preventive healthcare approach. This shift is driven by several factors, including the rising costs of healthcare, an ageing population, and the recognition that many chronic conditions are preventable through lifestyle changes and early interventions.
Eldercare facilities are increasingly offering programs focused on physical fitness, nutrition, mental health, and social engagement to help older adults maintain their health and independence. Additionally, advancements in technology and telemedicine are making it easier for seniors to access preventive care and monitor their health from home.
Comparing the advantages and disadvantages
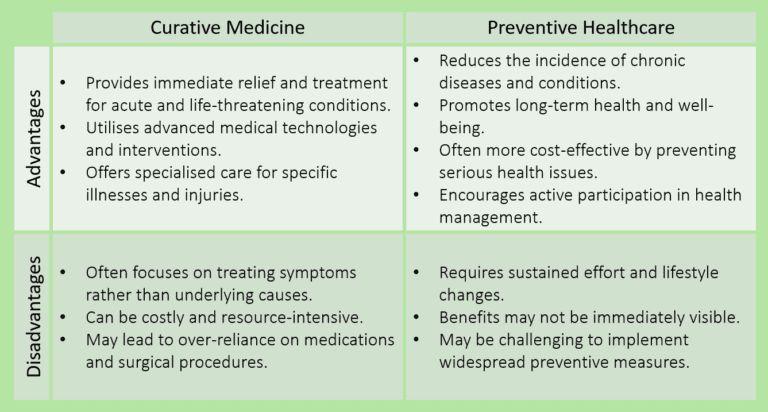
Curative Medicine
Advantages:
- Provides immediate relief and treatment for acute and life-threatening conditions
Curative medicine is essential for addressing emergencies and severe health issues that require prompt intervention. - Utilises advanced medical technologies and interventions
This approach leverages the latest medical innovations, such as surgeries and specialised treatments, to effectively manage complex health problems. - Offers specialised care for specific illnesses and injuries
Curative medicine involves experts who focus on particular areas of healthcare, ensuring that patients receive tailored and highly skilled care.
Disadvantages:
- Often focuses on treating symptoms rather than underlying causes
Curative medicine may address the immediate problem but not always the root cause, potentially leading to recurring issues. - Can be costly and resource-intensive
Treatments, hospital stays, and advanced medical procedures can be expensive and place a strain on healthcare resources. - May lead to over-reliance on medications and surgical procedures
Patients might become dependent on ongoing medical treatments and surgeries instead of exploring alternative, less invasive options.
Preventive Healthcare
Advantages:
- Reduces the incidence of chronic diseases and conditions
By focusing on prevention, individuals can avoid developing many long-term health issues, such as diabetes and heart disease. - Promotes long-term health and well-being
Preventive measures encourage healthier lifestyles, which contribute to sustained health and improved quality of life over time. - Often more cost-effective by preventing serious health issues
Preventing diseases can reduce the need for expensive treatments and hospitalisations, saving money for both individuals and healthcare systems. - Encourages active participation in health management
Preventive healthcare empowers individuals to take charge of their health through regular check-ups /screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices.
Disadvantages:
- Requires sustained effort and lifestyle changes
Maintaining preventive health measures involves ongoing commitment and may necessitate significant changes to daily habits and routines. - Benefits may not be immediately visible
The positive effects of preventive healthcare can take time to manifest, which might discourage some people from sticking with preventive practices. - May be challenging to implement widespread preventive measures
Ensuring that preventive healthcare is accessible and adopted by a large population can be difficult due to various barriers, such as socioeconomic factors and healthcare disparities.
Which model is better for today’s eldercare?
For today’s eldercare, preventive healthcare is increasingly seen as the more effective model. With the growing number of older adults, many of whom are living longer lives, the focus on prevention can significantly enhance their quality of life.
Preventive measures can help mitigate the impact of ageing-related diseases, reduce healthcare costs, and support seniors in maintaining independence and vitality. While curative medicine remains essential for treating acute and severe conditions, a balanced approach that prioritises prevention can lead to better overall health outcomes for the elderly.

Enhancing preventive healthcare
To do more on preventive healthcare, a multifaceted approach is necessary, involving individuals, communities, healthcare providers, and policymakers. Public health campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of preventive measures, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and routine health screenings. Educational programs in schools and workplaces can teach healthy habits early on and promote a culture of wellness. Healthcare providers can integrate preventive services into regular care by offering screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle counseling during routine visits. Policymakers can support these efforts by funding public health initiatives, improving access to preventive services, and creating environments that facilitate healthy living, such as safe walking paths and access to fresh produce. Technology also plays a crucial role; wearable devices and telemedicine can help individuals monitor their health and receive timely advice from healthcare professionals. By taking these steps, we can build a robust preventive healthcare system that not only reduces the burden of chronic diseases but also enhances the overall well-being of our current and future ageing population.
Conclusion
The shift from curative medicine to preventive healthcare represents a vital evolution in the approach to eldercare. By emphasising prevention, the eldercare sector can help older adults avoid many common health issues, enjoy a higher quality of life, and reduce the financial burden on healthcare systems. For the young-old population, adopting preventive healthcare practices can lead to a more active, healthy, and fulfilling life. As we move forward, it is crucial to continue integrating preventive strategies into eldercare to ensure that our ageing population receives the best possible care.
